Pharmacology
SANCOXIB
(Rofecoxib) is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug which is a
specific COX-2 inhibitor.
It exhibits
anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic activities in a number of
experimental animal models and numerous clinical trials. It acts by
blocking COX-2 and hence inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis and thus
relieves pain and inflammation
|
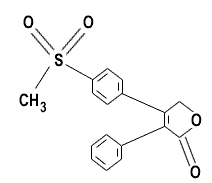
4-[4-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl]-3-phenyl-2[5H]-furanone |
|
The mean oral bioavailability of rofecoxib at
therapeutically recommended dose is approximately 93 percent. Rofecoxib
can be administered without regard to timing of meals. The peak plasma
level [Cmax] of 207±111 ng/ml
is achieved within 2-3 hrs after a single oral dose of 25mg. With multiple
dosing, steady state concentration is reached by day 4. Rofecoxib is
approximately 87 percent bound to human plasma proteins and the apparent
volume of distribution at steady state is approximately 91 L following
12.5 mg dose and 86 L following a 25 mg dose. Rofecoxib is metabolised
through reduction by cytosolic enzymes and the principal metabolic
products are the cis-dihydro and trans-dihydro-derivatives of rofecoxib.
Rofecoxib is eliminated predominantly by hepatic metabolism.
Approximately, 72 percent of the dose is excreted in the urine as
metabolites and 14 percent in the faeces as unchanged drug. The
effective half life t 1/2 (based on steady state level) is approximately 17
hrs.
Rofecoxib is approved for
the treatment of osteoarthritis, menstrual pain, dental pain and for
the management of acute pain in adults. It can also be used in a
variety of painful conditions including symptoms associated with influenza
or other viral infections, common cold, low back and neck pain, headache,
toothache, sprains and strains, myositis, neuralgia, synovitis. arthritis,
including rheumatoid arthritis, gout and ankylosing spondylitis, bursitis,
injuries, following surgical and dental procedures
-
Moderate to severe
hepatic in sufficiency.
-
Active peptic ulcer
disease.
-
Severe renal
impairment.
Rofecoxib should be prescribed with caution in
patients with a prior history of ulcer disease or gastrointestinal
bleeding. Use of rofecoxib is not recommended in patients with moderate or
severe hepatic insufficiency. It is important to monitor hepatic injury
parameters when using rofecoxib. Therefore, it is recommended that the
serum levels of liver function tests be assayed periodically when starting
rofecoxib for chronic use. Discontinue the drug immediately in cases with
worsening of liver tests. Rofecoxib should be prescribed with caution in
patients with impaired renal functions and preexisting asthma. Rofecoxib
should be prescribed with caution and should be introduced at lowest
recommended dose in patients with fluid retention, hypertension or heart
failure. Caution should be used when initiating treatment with rofecoxib
in patients with considerable dehydration. It is advisable to rehydrate
patients first before starting therapy with rofecoxib.
Dosage adjustment in the
elderly patients is not necessary. However, therapy with rofecoxib should
be initiated at the lowest recommended dose.
Rofecoxib has not been
investigated in patients below 18 years of age.
In late pregnancy,
rofecoxib should be avoided because it may cause premature closure of the
ductus arteriosus.
Rofecoxib is generally well tolerated. It has a lower
incidence of Gl tract side effects like irritation, ulcers and even
bleeding than other antiinflammatory drugs. The most common adverse
effects associated with rofecoxib therapy are upper respiratory
infections, diarrhoea and nausea. The other side effects are dizziness,
swelling of legs and / or feet due to fluid retention (edema), raised
blood pressure, indigestion, heartburn, headache or itchy skin. In
addition very rare, abdominal bloating, weakness, fatigue, mild allergic
reaction, skin rash or skin allergy may occur.
-
Rofecoxib may
diminish the antihypertensive effect of angiotensin converting enzyme
(ACE) inhibitors if given concomitantly.
-
Concomitant
administration of low dose of aspirin and rofecoxib may result in an
increased rate of Gl ulcerations.
-
When rofecoxib
and lithium are administered concurrently, subjects should be observed
carefully for signs of lithium
toxicity.
-
Standard monitoring of
methotrexate related toxicity should be continued if rofecoxib and
methotrexate are administered concomitantly.
-
When antacid and rofecoxib are
administered concurrently,Cmax of rofecoxib is decreased by 20%.
No data is available on event of overdose. It is
reasonable to employ the usual supportive measures e.g. remove unabsorbed
material from the gastrointestinal tract, employ clinical monitoring and
institute supportive therapy if required.
| Dosage and
administration |
The usual adult dosage of
rofecoxib is 12.5 to 25 mg once daily in osteoarthritis.For acute pain 50
mg once daily can be given to a maximum of 5 days.
Osteoarthritis :
12.5 mg once daily (in some cases, 25mg once daily may be recommended
)
Acute
Pain : 1st day : 50mg once daily
2nd day onwards : 25mg once daily
Disclaimer:
For the use only of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory.
| 


